Guide to Web Accessibility
Pixbrand Team
Published: 22/10/2023
- App Development
- Digital Marketing
- Ecommerce
- Seo
- shopify
- UI/UX Design
- Web Development
- woocommerce

Ever seen a library where not everyone can access the books on the higher shelf? The Internet is a digital library filled with books on communication, education, commerce and entertainment. Just like books placed on tall shelves, numerous website features and designs pose challenges for people with disabilities to access. Not everyone can easily reach or use these elements, creating barriers in the digital space Businesses should consider this space and improve the website accessibility for disabled users.
As per the World Health Organisation, over 1 billion people across the planet live with some form of disability. This includes hearing impairments (466 million), visual impairments (2.2 billion) disabilities (93 million), cognitive disabilities (240 million), and neurological disabilities (150 million). Due to incompatible technology and poor support, these individuals face diverse barriers to accessing and interacting with the website. Americans with disabilities act website compliance is a community that practises the content guidelines to ensure all Americans people with disability can access the information on all websites.
Such failure to access all the elements of a website goes beyond the user experience. It hinders their ability to participate fully in society by limiting their access to all opportunities. Businesses can lose a huge potential customer base due to the lack of inclusivity impacting their growth and profitability.
Pixabrand creates unique designs that are not only inclusive for people with impairments but also assist them to engage equally and become loyal customers of your business. Let’s learn and understand the WCAG guidelines 2.1 to ensure that every user is having a rich experience while visiting your website.
Definition of Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility refers to the practice of designing and developing websites in a way that is accessible and usable for people of all abilities and disabilities. It involves creating an inclusive digital environment that is easy to interact and navigate with everyone regardless of any cognitive or physical challenges. Web Accessibility defines the success of your business digitally.
Web accessibility means three things:
- Make your website accessible and usable for everyone, including people with disabilities.
- Backing up the available content for all to read and hear (like subtitles).
- Including assistive technologies like screen readers on your website
Importance of Accessibility for Disabled Persons:
For people with various disabilities, accessing digital content and services brings significant challenges when the website is not designed well with accessibility in mind. Suppose a person relies on screen readers to navigate a website and if the site is not properly coded or lacks alternative text for images, this person may struggle to fetch the correct information.
Web accessibility should be as per website content accessibility guidelines as it
- Ensures that individuals with disabilities can access digital content with the assistance of screen readers and easy-to-navigate layouts, ensuring equal access to information online.
- Promotes inclusion in various aspects of life that are reliant on digital interfaces like education, employment and social interaction. Everyone deserves an equal opportunity to learn and grow.
- Is mandated by the governments of many countries. These standards are not only about obeying legal obligations but reflect the values of inclusion, equality and social responsibility in a true manner.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Many countries have legal considerations and standards mandating web accessibility to ensure equal access to all. For instance, Americans with disabilities act website compliance in the United States and the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines established by the Wide Web Consortium set standards that all businesses must follow while developing their digital platform.
To establish inclusivity and from an ethical standpoint, web accessibility goes beyond legal compliance. It is a moral practice to create an online environment that is inclusive and offers equal opportunities to all. Regardless of the disabilities of an individual, the efforts to make an equal and dignified space for all. It is not only in the favour of some people but also in favour of businesses that are running on a global level and want to provide the best experience to all their customers.

Understanding Disabilities
A. Types of Disabilities
There are numerous visual, hearing and cognitive impairments that individuals suffer from. Here are the 5 major disabilities that cover all impairments:
- Visual impairments
- Hearing impatiens
- Motor Disabilities
- Cognitive Disabilities
- Neurological Disabilities
B. Impact of Disabilities on Digital Interaction
In the world of such advanced technology, limitation on website accessibility for disabled users is nothing less than a failure to provide a rich user experience and understand the requirement of inclusivity as a business. Different types of common disabilities and how they impact the users while accessing a website:
1. Visual Impairments
There is a common misconception among people about making websites for blind users who use screen readers. However, it’s not only about such blindness only, but also about people who have other visual impairments. While developing a website, consider these three major visual problems.
Moreover, the web accessibility issues for a sight-impaired audience are low contrast, low vision and colour blindness.
2. Hearing Impairments
A common assumption is that people with hearing impairments have fewer limitations on the web as compared to other disabilities. Even though such people can access the visual content and navigate, audio still poses a challenge. Preparing transcripts for the audio and videos can make them feel more inclusive and provide seamless browsing time.
3. Motor Disabilities
Users who have no hearing or seeing disability, might face difficulty controlling the mouse or keyboard and have physical disability. Voice controls, eye-tracking, smooth navigation, mouth sticks or Puff n Sip systems make the website accessible.
4. Cognitive Disabilitiess
Any mental or psychological condition that affects cognition falls under this type of disability. For instance, people who suffer from deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) face difficulty in focusing on one task for a longer period or learning new things. Designing a website that is easy to access, smooth to navigate and simple to remember, provides a seamless experience beyond disabilities.
5. Neurological Disabilities
Flickering, blinking or moving elements is the common content on websites to draw attention to particular parts. However, it fails when it comes to the audience who have neurological disabilities like photosensitive epilepsy or seizures.
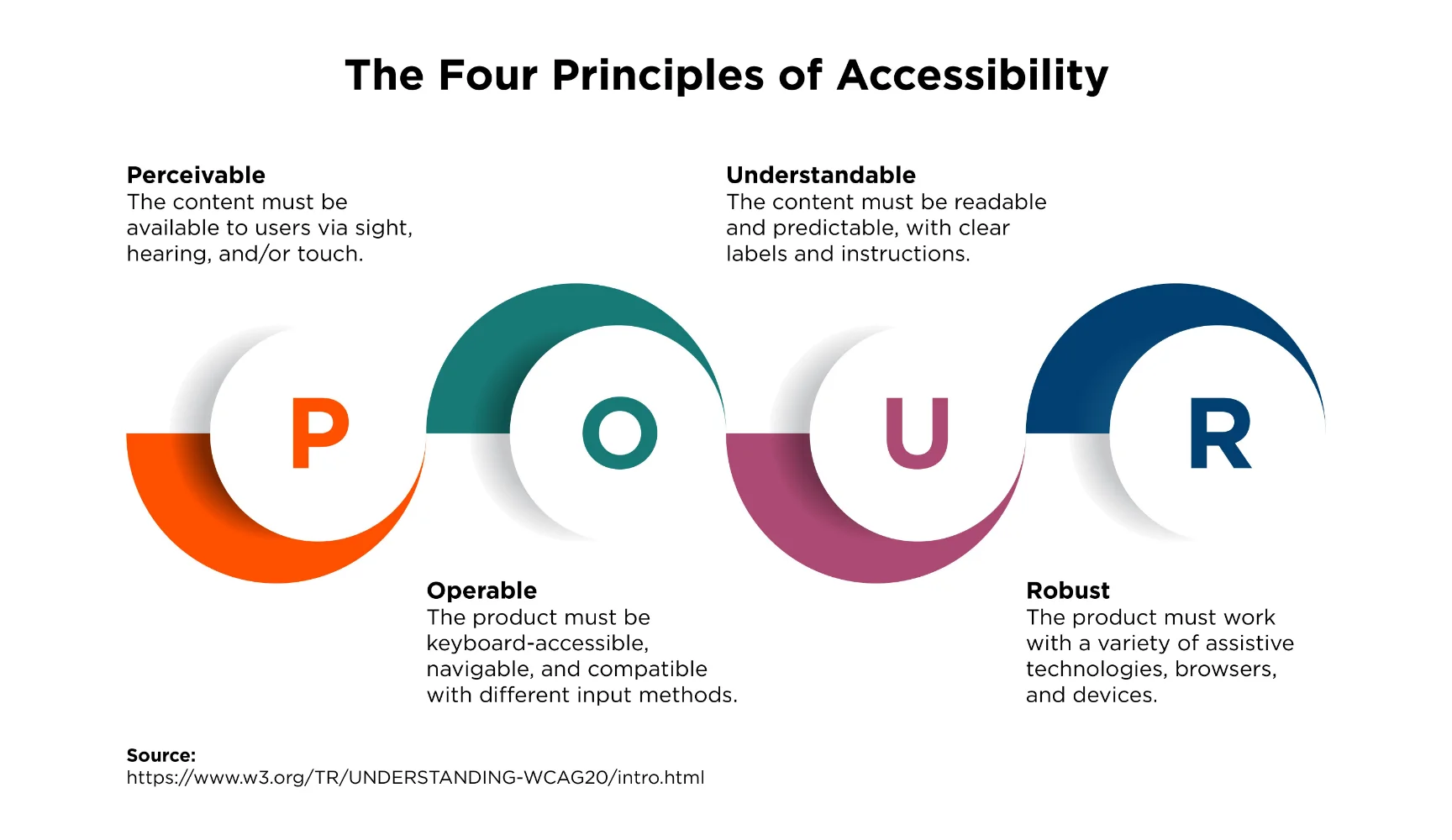
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
A. Overview of WCAG
Website Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is made by the Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to provide a roadmap to businesses to build web content that is perceivable, operable, understandable and robust for all users including those with disabilities. These four key principles of WCAG are the standard to design websites or any other digital platforms that accommodate diverse user needs and promote inclusivity. It not only follows legal compliance but also promotes ethical principles in digital space to make it equally accessible for all.
B. Key Principles of Accessibility
1. Perceivable
Information and content must be presented in such a way that it can be perceived by users in their own ways. People who are blind or have low vision use screen readers that convert the printed text into audio or braille characters.
2. Operable
From navigating a page to selecting a link from the menu or playing/pausing the video, all the elements on your web page should be easy to utilize. Keep the website simple and ditch any extra functionality that can create a distraction for disabilities.
3. Understandable
Text content, graphic design content and media, all types of content must be easy to read for the website visitors. Elements like jumbled words or verbose language create a challenge for visitors who have cognitive difficulties and also, people who can’t speak the predominant language of your website.
Organise your pages intuitively and easy to navigate for all visitors.
4. Cognitive Disabilitiess
Any mental or psychological condition that affects cognition falls under this type of disability. For instance, people who suffer from deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) face difficulty in focusing on one task for a longer period or learning new things. Designing a website that is easy to access, smooth to navigate and simple to remember, provides a seamless experience beyond disabilities.
5. Robust
All the content on your website should be easily interpretable and consumable by all visitors including those who are using screen readers. To make it accessible, write an HTML code that allows the assistive technologies.
C. Guidelines for Text, Images, Forms, and Multimedia
From offering text readability and semantic structure to creating images, forms and multimedia that are accessible to all, these guidelines ensure that the web page is inclusive and accessible to all.
Text: Guidelines
- Easy-to-read text with an appropriate font, size, and contrast ratio
- Alternative text for images to convey the content to visually impaired users
- Proper HTML tags to create a logical reading order for assistive technologies
- Use simple language and avoid jargon benefiting people with cognitive disabilities
Image Guidelines
- Descriptive text for images, conveying their meaning and functionality
- For decorative images, use null or empty alt text to ensure screen readers can focus on essential content
- Long descriptions or image captions to provide detailed information
Forms Guidelines
- Form fields must have clear labels, instructions and error message
- Ensuring that people with motor disabilities can fill forms using the keyboard or any other respective device
- Identifying errors and providing suggestions for correction for users with cognitive disabilities
Multimedia Guidelines
- Include captions and transcripts for audio and video content, helping users with hearing impairments
- Audio descriptions for visual elements in videos for the visually impaired
- Ensure media players have controls and are operable via keyboard to navigate easily
Testing for Accessibility
A. Manual Testing
Manual testing is one of the ways to identify and address the accessible issue on your website that might fail to be accessed by automatic tools.
1. Keyboard Navigation
This testing includes interaction with a website or app using a keyboard. It ensures that users who are relying on assistive technologies like screen readers can easily navigate the interface.The key focus of such testing is
- All elements are in logical order and easy to navigate.
- Adding skip links to jump on the main content or navigation area
- All the interactive elements like buttons or links are focusable.
2. Screen Reader Testing
This testing includes the usage of screen readers to know the experience a visually impaired will have while accessing your website. Screen readers guide the content and structure by vocalising.
Key aspects of Screen Reader Testing:
- The website should be compatible with most common screen readers
- Adding alternative text for images and non-textual elements
- Checking whether there is a use of heading to give a proper structure to the content
3. Color Contrast Checks
Colour contrast testing is about evaluating the contrast between the background and foreground colours. This is done to ensure that text and other visual elements are easy to distinguish for users with colour blindness or poor vision.
- Use of colour control tools to measure contrast ratio
B. Automation Tools For Accessibility Testing
The other way of testing web accessibility is by using website accessibility testing tools. W3C has mentioned the list of tools that can be used to test the website based on the different guidelines. Here are a few tools to use and examine the accessibility of elements and content on the web.
1. Introduction to Tools (e.g., Axe, WAVE, Lighthouse)
Here are the most widely used automatic tools
Axe –
A comprehensive accessibility testing tool by Deque Systems. It is available as both a JavaScript library and a browser extension. To use the tool, either install it as the browser extension or integrate it with the JavaScript library into your development workflow. It will automatically scan your website and find out the issues.
Axe helps to identify
- Colour contrast issues
- Keyboard navigation issues
- Screen reader compatibility issues
- Alternative text issues
WAVE –
Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool is a free online tool by WebAIM that offers quick testing and generates reports in detail. To use WAVE, enter the website URL you want to test. It will scan the website and generate a report highlighting the accessibility issues.
WAVE helps to identify
- Colour contrast issues
- Heading structure issues
- Alternative text issues
- Link structure issues
Lighthouse –
An open-source website accessibility testing tool by Google to integrate and audit along with checking SEO performance. To use it, install the extension of Lighthouse for Chrome or try the Lighthouse CLI tool. Run the tool to generate a report that finds the accessibility issues, web performance and SEO audits.
Lighthouse helps to identify
- Colour contrast issues
- Heading structure issues
- Alternative text issues
- Keyboard navigation issues

Assistive Technologies
A. Overview of Assistive Technologies
Assistive technologies play a vital role in enabling individuals with disabilities to access and interact with digital content. These tools provide alternative means of input, output, and navigation, facilitating the use of computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices.
1. Screen Readers
Screen readers are software applications that convert visual text into synthesised speech or braille output. It allows visually impaired individuals to navigate and interact with the web interfaces, The most common screen readers are JAWS, NVDA and VoiceOver.
2. Voice Recognition Software
A software to convert the spoken language into text. It assists the motor or speech impairments to interact with computers via voice commands. The most popular software are Dragon, NaturallySpeaking and Google Speech to Text.
3. Braille Displays
A refreshable output device that translates the text into braille characters, so visually impaired users can read and interact with text-based content. Focus 40 Blue and Orbit Reader 20 is some of the most popular Braille Displays.
B. Designing for Compatibility with Assistive Technologies
Web developers and designers are the soul of an accessible web development team. Pixa Brand is a branding and UI interface-building agency that follows the accessibility guidelines and incorporates them to design your website. They practise website content accessibility guidelines in all the types of work they do.
1. ARIA Roles
ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) is a set of attributes that web developers can use to define the roles and relationships of interactive elements on a web page. These attributes provide additional context for assistive technologies, allowing them to better understand the purpose and function of each element.
2. Focus Management
Focus management is the ability to control which element on a web page is receiving user input at present. Assistive technologies rely on focus management to help users navigate and interact with elements in a predictable manner.
Developers should make sure that focus is indicated and must be controlled via keyboard or any other assistive technology input methods.

Importance of User Testing
A. Involving People with Disabilities in the Testing Process
The first-hand experience of people with diverse disabilities can provide invaluable insights into the inclusivity and accessibility of the website. With their help, developers can get a deeper understanding of the challenges and can develop customised solutions as per their respective needs.B. Gathering Feedback and Iterating
User testing is not a one-time process, it is an iterative process to gather feedback from users with disabilities and implement it to make improvements. The continuous cycle of testing, feedback, and refinement ensures that all your latest elements are equally effective and accessible to the users. It is the best way to keep your web accessible throughout the time while letting all users easily navigate and interact with the designs.C. Real-World Accessibility Challenges
Numerous things can go unnoticed during web development. Real-world accessibility gives you real-time insights about the possible challenges faced by any user. It helps you to build a more inclusive environment for everyone.Case Studies
A. Successful Implementation of Accessibility
There are many businesses implementing accessibility guidelines to make their platform accessible to all. Let’s know about such businesses
Microsoft
Microsoft is one the greatest examples that fulfilled the commitment to accessibility by integrating into its products, services and internal processes. They have established an Accessibility Centre of Excellence to provide resources training and support to developers and designers.
They frequently involve individuals with disabilities in the development process through user testing and advisory roles. This made huge improvements in enhancing the accessibility of their products including Windows, Office and Azure.
Adobe
Adobe ensured that all their products like – Photoshop, Illustrator and InDesign are accessible to users with disabilities. They include practices like keyboard navigation support, alternative text for images and colour contrast adjustments to make their product line more inclusive.
Besides this, Adobe has extensive documentation and training materials to help individuals with disabilities to maximise the use of their products.
B. Challenges Faced and Overcome
Netflix
Netflix faced accessibility challenges with their video player and navigation controls making it hard for visually impaired users to interact with the platform. They addressed these challenges by implementing keyboard navigation, including detailed alternative text for videos and improving the contrast between bg elements and text.
The platform was initially facing challenges in making their platform accessible to all users, especially those who use screen readers. The dynamic nature of Twitter and the use of JavaScript made it difficult for assistive technologies to interpret and navigate the content.
Then Twitter invested in resources like collaborating with users with disabilities and assisting technology experts to enhance accessibility.
They have implemented keyboard navigation, alternative text for images and support for screen readers.
Conclusion
Web Accessibility goes beyond the legal obligation of the guidelines made by WCAG to make the website accessible for all. It is an ethical practice that should be done by every business owner to ensure that all users have a rich user experience.
The four principles of WCAG guidelines 2.1 ensure that all types of content – text, images, videos, forms etc. are easy to consume and navigate by people who have any kind of disabilities. Also, there are numerous automation tools for accessibility testing as per guidelines available to check if any website is missing the content rules for visual or hearing-impaired people.
It is a kind of social responsibility that every business should work on not only to make things inclusive but to create an impactful brand impression.
Pixabrand is one the leading branding agency that is aware of all the guidelines and they ensure that their web designs are accessible by all.